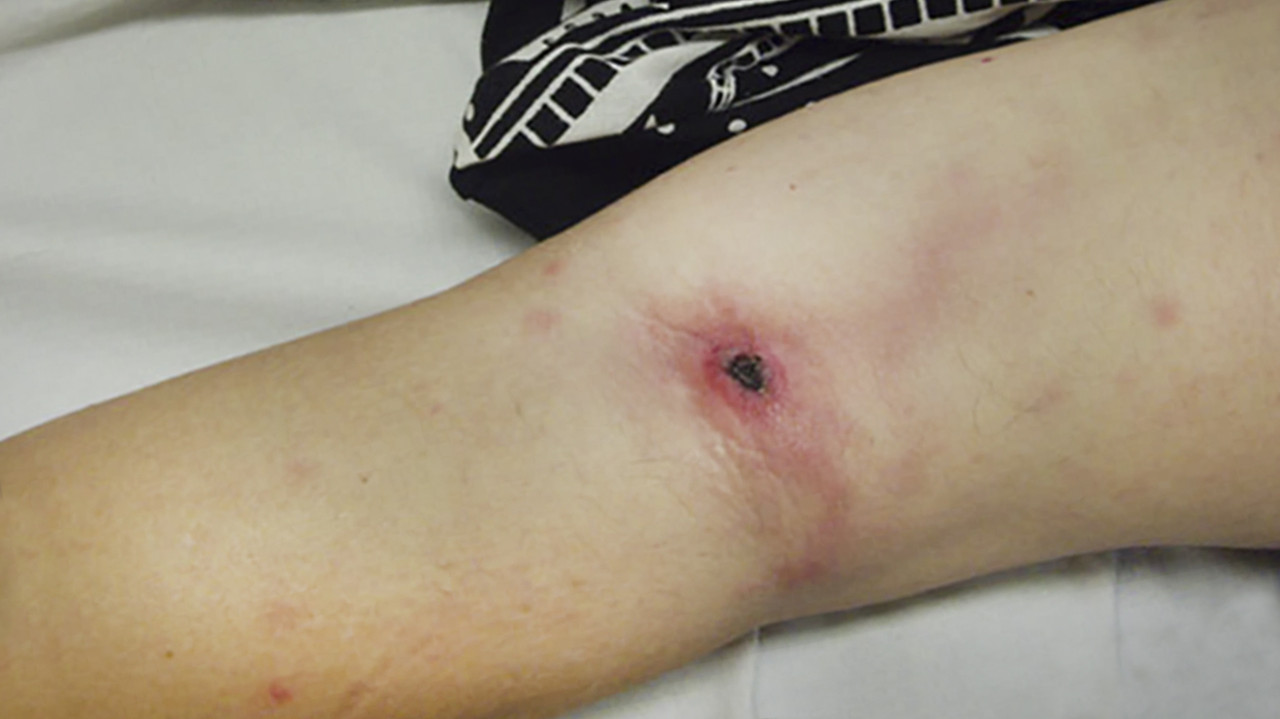
Skin abscesses are painful collections of pus that develop due to bacterial infections. Black salve, with its potent natural ingredients, is an effective remedy for drawing out pus and promoting healing in abscesses. Here’s a step-by-step guide on using black salve for treating skin abscesses.
Benefits of Black Salve for Skin Abscesses
Black salve contains powerful ingredients like bloodroot and zinc chloride, which have been traditionally used for their drawing and healing properties. These components help draw out the pus from abscesses, making it a natural and effective treatment.
1. Cleaning the Area: Start by thoroughly cleaning the abscess area with warm water and soap. This step is essential to remove any bacteria and prepare the skin for treatment.
2. Applying Black Salve: Apply a small amount of black salve directly to the abscess. The salve’s active ingredients will begin to penetrate the skin, working to draw out the infection.
3. Covering the Abscess: Cover the treated area with a bandage to keep the salve in place and protect it from external contaminants. Leave it on for several hours or overnight.
4. Checking and Draining: After several hours, check the abscess. If the pus has been drawn to the surface, gently clean the area and use sterilized tweezers to remove any visible core. If the abscess has not drained completely, reapply the black salve and cover it again.
5. Post-Treatment Care: Once the abscess has drained, clean the area again with warm water and soap. Apply a soothing ointment to promote healing and prevent infection. The anti-inflammatory and antiseptic properties of black salve aid in reducing swelling and keeping the area clean.
Conclusion
Using black salve for skin abscesses is a natural and effective method to treat infections and promote healing. By following these steps, you can safely manage skin abscesses at home. For more detailed information, refer to the original article: Effectively Utilizing Black Salve for Boil Treatment.
Disclaimer
This article is for informational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. Consult a healthcare professional for diagnosis, treatment, and specific medical advice.